Knowing the regulations regarding child’s car seat is vital to ensure our young passengers’ safety. The vast state of Texas—known for its wide landscapes hosting numerous roads—often triggers questions about when children are allowed to sit in the vehicle’s front seat. The transition from the rear to the front seat isn’t just about convenience—it’s largely about safety. This article will delve into the guidelines outlined by Texas law that are intended to aid parents or guardians in deciding the right time for their children to accompany them in the front seat during travels. We will discuss comprehensively from the lawful provisions to the best methods for devising a safe yet cozy trip environment for both child passengers as well as adults.
At What Age Can Kids Sit in the Front Seat of a Car in Texas?
Texas stipulates regulations on when children can occupy a car’s front seat based on aspects like age, height, weight with the primary focus being safety. Local laws declare that unless their height exceeds 4 feet 9 inches kids under 8 years must be strapped into a Child Passenger Safety Seat System.
There are no explicit restrictions when it comes to age to sit in front as per car seat law, Texas. However, an important point to underscore here is that though the car seat law in Texas does not stipulate when can a chid sit in the front seat in Texas, it is generally advisable to reserve the passenger seats for them until they turn at least 13 years old. The backseat offers increased security particularly in situations involving an accident where airbags deploy.
In the end the determinant of when can a child sit in the front seat in Texas should not be solely their physical stature or children ages but also their degree of maturity coupled with their ability to abide by safety recommendations while sitting inside car as proposed by specialists. The safety of children must always take priority while driving with them.
Height and Weight Requirements for Sitting in the Front Seat
Determining the appropriate time for a child to occupy the front seat of a vehicle isn’t simply a matter of height and weight requirements for front seat, Texas. A consideration of other safety guidelines is also crucial. As previouysly mentioned, there’s no specified age as to how old to sin in front seat, Texas. However broadly speaking children are advised to stay in the back seat until they cross the age of 13.
When it comes to considering weight or height safety experts suggest that a child should be 4 feet 9 inches tall minimum along with an approximate weight of 80 pounds before they sit in the front seat without a booster seat. This advice is to make sure that the child is tall enough for the seatbelt to fit correctly as well be shielded by other safety systems in the car including airbags to avoid any personal injury.
The above-mentioned weight or height guidelines are general recommendations which may change depending on the individual child’s development along with specific circumstances. For making decisions regarding children’s safety it’s pivotal for parents to take into account different factors such as the child’s size maturity etc. They should also follow the advice of safety experts as well as the local laws.
Child Safety Tips In Motor Vehicles
The well-being of children when car travelling is fundamentally important in reducing the possibility of them getting harmed. Here are vital factors to bear in mind concerning child safety:
Child Restraint Systems: Utilizing suitable child restraint systems is pivotal. These systems can be car seats, front facing car seat, belt positioning booster seat, booster seats or seat belts, shoulder seat belt or lap and shoulder belts that are selected based on a child’s age, stature or mass. Install the car seat correctly, and always comply with the instructions given by the manufacturers as well as adhering to the legal regulations on child restraint use in your area.
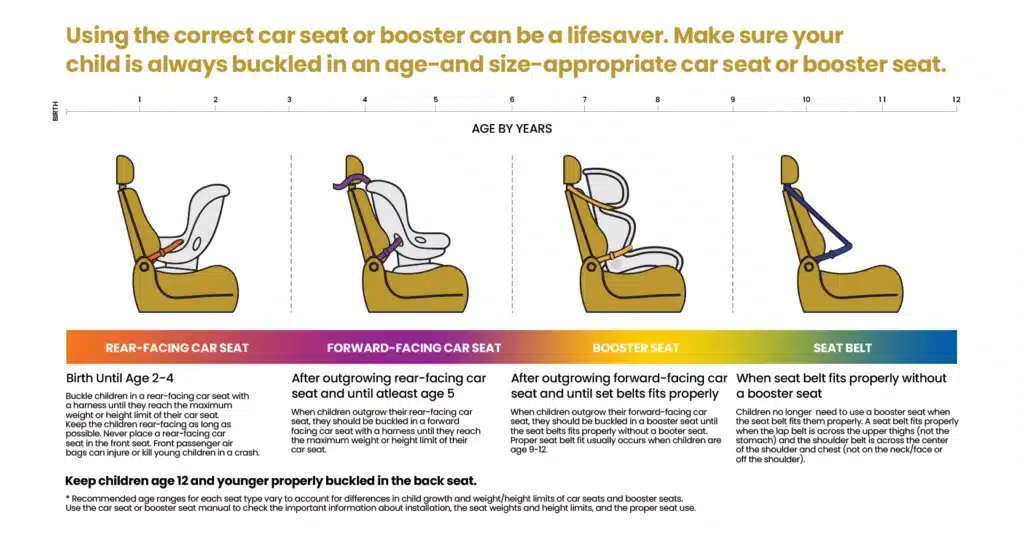
Rear-Facing Car Seats: For prolonged safety measures for infants or young children during travel, it is best to have them seated in rear-facing car seats until they reach the maximum limit of the seat’s height or weight capacity as advised by manufacturers. This particular orientation provides exceptional care towards the nurturing bodies of children by offering support notably to their heads, necks backbones.
Forward-Facing Car Seats: Following the outgrowing stage of a rear-facing seat by a child; they may proceed to use the forward-facing car seat that comprises a harness. It is vital to confirm that the seat is fixed correctly in position with assurance that the harness is taut – with the chest clip located on the same level as the armpit.
Booster Seats: When a child outgrows a forward-facing seat, a booster seat should be used until they reach the recommended height and weight to use a seat belt alone. The booster seat helps position the seat belt properly across the child’s body, providing adequate protection.
Seat Belt Use: When a child is ready to transition from a booster seat to using a seat belt alone, ensure that the seat belt fits correctly. The lap belt should lie low across the hips, touching the upper thighs, while the shoulder belt should cross the center of the chest and shoulder.
Safety with Airbags: It’s crucial that children refrain from occupying seats in front of a live airbag as it can present severe dangers if an accident occurs. For children who are under the age of 13 years old the rear seat is considered the most secure place.
Regular Seat Checks: Routinely check and adjust the installation of child safety seats to ensure they are securely fastened. Consult the seat manufacturer’s instructions and consider having the installation verified by a certified child passenger safety technician.
Lead by Example: Always wear your adult seat belt and ensure that all passengers, including children, are properly restrained, with the car seats installed correctly. Children are more likely to follow safety practices if they see adults consistently using seat belts.
Bear in mind that guaranteeing child safety during car journeys is a collective duty of parents or guardians as well as motorists. Through the observance of these regulations we can work towards ensuring the safety of our precious little ones while also promoting safer travel for all passengers.
Types Of Seats And Safety Devices For Kids
There are several types of seats and safety devices available to ensure the protection and well-being of children in motor vehicles. Here are some commonly used options:
Rear-Facing Infant Car Seats: Designed for infants and young babies, these seats are positioned in a rear-facing orientation. They provide crucial support for the head, neck, and spine and should be used until the child reaches the seat’s height and weight limits or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Convertible Car Seats: These seats can be used in both rear-facing and forward-facing positions, accommodating a child’s growth. They typically have higher weight and height limits than infant car seats, allowing for extended rear-facing use and transitioning to forward-facing when appropriate.
All-in-One Car Seats: Also known as 3-in-1 or extended-use car seats, these versatile seats can be used in multiple configurations: rear-facing, forward-facing, and as a booster seat. They offer longer usability, accommodating children from infancy to booster seat stage.
Booster Seats: Texas booster seat weight requirements stipulate that the child must be at least 4 years old and weighed at least 40 pounds. Booster seats elevate a child’s seating position, allowing the seat belt to fit properly across their body. There are high-back boosters that provide head and neck support and backless boosters for older children. They are used once a child has outgrown a forward-facing seat and until they can safely use a seat belt alone as stipulated in the Booster seat laws, Texas.
Combination Seats: These seats combine a forward-facing harness seat with a booster seat, offering a transition from a harness to a seat belt as the child grows. They provide convenience and cost-effectiveness by serving two purposes.
Seat Belt Positioning Devices: These devices, such as belt-positioning booster seats or seat belt adjusters, are designed to optimize the fit and positioning of the seat belt on a child. They help ensure that the lap belt lies low on the hips and the shoulder belt crosses the chest and shoulder correctly.
It is important to note that regardless of the type of seat or safety device used, they must meet safety standards and be installed and used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Additionally, regular checks of the seats for proper installation and adjustments are crucial to maintain their effectiveness.
Always refer to local laws and guidelines and consult with certified child passenger safety technicians for expert advice on selecting and using the appropriate seats and safety devices for your child’s age, height, and weight.
Tips When Using Child Car Seats
Choose the Right Seat: Select a car seat that is appropriate for your child’s age, height, and weight. Ensure that the seat meets safety standards and is compatible with your vehicle.
Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Read and understand the instructions provided by the car seat manufacturer. Proper installation and usage are crucial for optimal safety.
Install Correctly: Install the car seat according to the manufacturer’s instructions and your vehicle’s owner’s manual. Make sure it is securely and tightly installed using either the vehicle’s seat belt or the LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) system, if available.
Rear-Facing as Long as Possible: Ensure your child remains in a car seat facing backward for the greatest duration feasible. Observe the height as well as weight restrictions fixed by the maker. This orientation offers superior safeguarding for their head, neck due to more supportive alignment of the spine.
Harness Straps: Adjust the harness straps to fit snugly over your child’s shoulders. The straps should lie flat with no twists and should be positioned at or below your child’s shoulders for rear-facing seats and at or above for forward-facing seats.
Chest Clip Placement: Position the chest clip at armpit level to ensure proper placement and effectiveness of the harness straps.
Harness Tightness: Ensure that the harness straps are appropriately tightened to eliminate slack. You should not be able to pinch any excess strap material.
Seat Position: Place the car seat in the back seat of the vehicle whenever possible. It provides the most protection, especially in vehicles equipped with a passenger airbag.
Regular Inspections: Regularly check the car seat for proper installation and any signs of damage or wear. Inspect the harness and buckles to ensure they are in good working condition.
Register the Car Seat: Fill out and submit the registration card for your car seat. This enables the manufacturer to contact you in case of any recalls or safety-related updates.
Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest safety guidelines, regulations, and recommendations regarding child car seats. Consult with certified child passenger safety technicians for expert advice and assistance.
Texas Car Seat Laws
Rear-Facing Car Seat: The law in Texas mandates that children below two years old or those not meeting the manufacturer’s stipulated height or weight guidelines must be secured in a car seat facing the rear. For optimal safety, children should remain in this position for the duration recommended by the maker.
Forward-Facing Car Seat: Once a child outgrows the size limitations of the rear-facing car seat, they should be moved to a forward-facing car seat that features a harness system. Manufacturer guidelines regarding weight limits, height limits, age should always be adhered to when utilizing these seats.
Booster Seat: According to Texan law, children no longer fitting into a forward-facing car seat yet who are shorter than 4 ft 9 inches must make use of a booster seat. Booster seats assist in accurately positioning the car’s seat belt across the child’s form for optimal protection.
Seat Belt: Children who are too big for booster seats yet still below 17 years of age must wear a seat belt as per Texas law. It’s crucial to ensure the seat belt is fitting correctly – the lap part should be lying low against the hips with the shoulder strap resting across the chest area.
Front Seat: Although Texas law doesn’t clearly define an ideal age for kids to sit in the front seat of a vehicle. It’s generally considered best to keep them seated in the rear until at least 13 years old due to improved protection that back seats provide particularly in vehicles fitted with airbags.
What Are The Penalties Of Child Car Seat Law Violations?
Not adhering to child car seat laws can incur heavy penalties in many states including Texas. The exact penalties can alter based on different factors such as previous offenses or violation specifics.
For example, breach of child passenger safety laws in Texas might result in fines from $25 to $250 for first offenders. Repeating offenses will lead to more severe penalties like increased fines or additional consequences like mandatory court appearances or drivers license suspension.
Child safety should be a priority always; ensure adherence to related car seat laws to protect them during travels. Stay updated with latest information from trusted sources or ask local authorities about specific penalties if child car safety laws are violated in your region.
What Are The Requirements To Sit In The Front Seat Of A Car in Dallas, Texas?
Generally speaking, the guidelines for occupying the front seat of a vehicle usually depend on factors like age, height, weight, as well as local laws. Nevertheless, it’s crucial to understand that certain jurisdictions may not stipulate explicit age criteria for sitting upfront in a car; the advice may differ.
In a bid to protect children’s safety optimally, it’s typically advised to have them seated in the rear until they attain a minimum age of 13 years. This advice is grounded on the fact that the back seat offers improved safety features particularly in cars fitted with airbags.
Are There Any Exceptions To The Rule?
Yes! Under select situations, the rule about children sitting in back seats till they attain a determined age could waver like the following:
Medical Issues: Occasionally there might be situations where due to particular health conditions or disabilities a child might need to be positioned or supervised in the front seat for medical or safety considerations. This would usually be under the guidance of a medical healthcare professional.
Vehicle Constraints: If for some reason a vehicle lacks a back seat or is unsuitable for child seat installations then an exception allowing a child to sit up front might be given. This could apply to certain makes of trucks or older vehicles that have no back seating.
Overcrowded Rear Seating: In circumstances where there are more children than rear seating accommodations permit in a vehicle, like a carpool, an exception might be given to allow a child to sit up front. Safety should be of primary concern here ensuring the child is correctly secured based on their age size or weight.
Parental Judgement: In certain scenarios parents might be given the discretion to decide when their child may sit upfront based on their maturity level size or other relevant factors. Parents need to make decisions regarding their child’s safety keeping in mind all relevant laws guidelines as they do so.
Why Are Airbags Dangerous For Children?
Children face heightened danger from airbag technology since inflators operate aggressively upon impact, capable of inflicting injuries. Here are some reasons why airbags, like the F150 air bags, can pose a risk to children:
Deployment Force: Deployed with remarkable force, airbags act as efficient shock absorbers for grownup passengers. However, this may be too much for younger ones with growing frames. While airbag deployment can protect adults, childhood exposure elevates injury danger through inflation pressure.
Proximity to the Airbag: Kids’ shorter stature results in them sitting closer to the safety features. Proximity intensifies collision danger, heightening damage probability. Childhood safety may be compromised due to rapid inflation causing wounds in any of these regions.
Improper Restraint: An elevated danger arises if insufficient security in a traveling vehicle. A child who is not properly secured will likely slide forward upon impact, resulting in greater chance of collision with the airbag.
Size and Development: The bones, muscles, as well as the ligaments of young kids are still in the developmental stage hence they might not be able to endure the impact of an inflating airbag. Moreover their petite frames have less mass to diffuse the strike making them increasingly prone to injuries.
To mitigate the risks associated with airbags, it is important to follow recommended safety practices:
- To maximize security, make sure you secure your little ones by employing the right seating arrangements.
- In situations where safety is paramount, relocate children toward the rear section.
- To ensure a safe journey for your little ones, adhere strictly to child passenger security system installation and usage protocols.
- For maximum safety during travels, adhere to the seat producer’s instructions regarding rear-facing placement duration.
- Keep track of the area and job of airbags inside your motorcar together with following the directions laid down by the maker for optimal safety results.
Typical Child Injuries in Car Accidents in Texas
In vehicular accidents involving children in Texas or elsewhere can lead to a variety of injuries based on the accident’s specifics. Below are common injuries kids might suffer in car accidents:
Brain Damage: Children’s skulls are still maturing which makes them especially vulnerable to brain injuries. These injuries can vary from minor concussions to major traumatic brain damage. The latter could result in lasting cognitive impairment or changes in behavior.
Neck or Spine Damage: Neck or spinal injuries such as whiplash are typical in car accidents. Given children’s continuing growth in these areas they are more exposed to sprains or fractures that may even lead to partial or full paralysis.
Chest or Abdominal Injuries: The force of a collision might injure a child’s chest or abdomen. This might result in injuries affecting internal organs such as broken ribs or damages to the liver or lungs which might need urgent medical intervention.
Extremity Injuries: Due to a car crash a child might have various injuries ranging from relatively minor to severe on their limbs such as fractures or sprains on arms or legs.
Injuries to the Face: Impact with the dashboard or airbags can lead to facial damages. Children might experience fractures in their facial bones or damage to their jaws or eyes.
Mental Trauma: Car accidents can also have a substantial psychological impact on children resulting in conditions such as PTSD or anxiety disorders among other emotional traumas if not addressed properly.